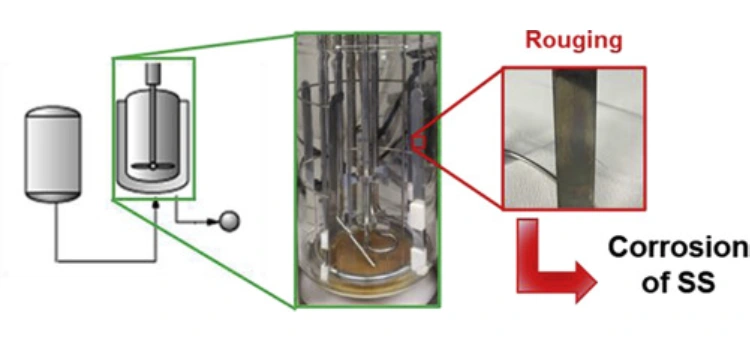
Stainless steel (SS316L) is the backbone of the pharmaceutical industry due to its high corrosion resistance, low carbon content, and exceptional purity standards. Yet, even this robust material is vulnerable to a subtle but dangerous form of deterioration: rouging. When left unchecked, rouging can compromise the quality of pharmaceutical products, decrease the operational efficiency of clean-in-place (CIP) systems, and lead to costly regulatory violations.
05
AugUnderstanding Rouging and Corrosion in SS316L Pipes in Pharma Industries
In this comprehensive blog, we explore the science behind rouging, its link to corrosion, and the role of cleaning, derouging and passivation in maintaining pharmaceutical-grade pipelines. We'll also look at key mitigation strategies using modern chemistry and techniques that meet stringent compliance standards.
What is Rouging?
Rouging is a form of discoloration or surface deposit on stainless steel, usually reddish-brown, caused by the oxidation of iron. Despite the corrosion-resistant nature of SS316L, trace amounts of iron can still oxidize under specific environmental conditions. Rouging is not merely an aesthetic concern—it can signify the breakdown of the protective chromium oxide layer that shields stainless steel from chemical attack.
There are three commonly recognized types of rouging:
- - Type I: Iron oxide deposits from external sources (common in newly commissioned systems).
- - Type II: Iron oxide layers formed from corrosion of the stainless steel surface itself.
- - Type III: Often seen in high-purity water systems, resulting from chromium and iron oxide formations.
Each type can interfere with the purity of pharmaceutical fluids, making it essential to identify and mitigate rouging early.
Root Causes of Rouging in Pharma Pipes
- 1. High-Temperature Water or Steam Exposure SS316L reacts when exposed to high-purity water or clean steam at elevated temperatures, a common practice in pharmaceutical manufacturing. These conditions gradually strip away the chromium oxide layer and promote iron oxidation.
- 2. Chloride-Induced Corrosion Pharmaceutical plants often struggle with trace amounts of chloride ions, which aggressively attack stainless steel. This chloride attack initiates pitting corrosion, creating localized weak spots that facilitate rouging.
- 3. Improper Passivation and Surface Finish Surfaces that are not adequately passivated—or those that have rough finishes—are more prone to harboring microscopic crevices. These crevices can trap moisture and promote corrosion. In such cases, derouging and passivation treatments become necessary to restore surface integrity.
Why Rouging is a Critical Issue in Pharma
Regulatory bodies like the USFDA and EMA require pharmaceutical manufacturers to follow strict Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). This includes controlling contamination risks from pipelines and equipment. Rouging deposits can:
- - Flake off into process fluids, causing product contamination
- - Alter pH and conductivity readings
- - Harbor biofilms or microbial contamination
- - Reduce heat transfer efficiency in systems
- - Lead to equipment failure or costly downtime
Hence, periodic Cleaning and Passivation in Pharma facilities is not just recommended—it's essential.
Detecting and Diagnosing Rouging
Early-stage rouging is often hard to detect visually. That's why advanced techniques are employed:
Visual Inspection: Identifies visible surface discoloration.
Swab Testing: Measures trace iron contamination.
XPS/AES Analysis: Provides elemental composition of the passive layer.
Free Iron Testing (Ferroxyl Test): Determines surface contamination levels.
These evaluations are critical to deciding when derouging solutions and service are needed.
How to Prevent and Remove Rouging
- Step 1: Pre-cleaning with Eudragit Polymer Cleaner (if applicable) In cases where pharmaceutical formulations or coatings (like Eudragit-based drugs) are processed through the lines, pre-cleaning with an Eudragit Polymer Cleaner is recommended. These specialty cleaners dissolve polymeric residues before initiating metal surface treatment.
- Step 2: Descaling and Derouging A Descaling Service involves removing heavy oxide layers and mineral scales before derouging. Derouging chemicals like citric acid-based gels or specialized formulations are used to strip rouge without damaging the substrate.
- Step 3: Passivation Passivation follows derouging and is designed to restore the chromium-to-iron ratio on the surface. This process rebuilds the protective chromium oxide film, reducing the chances of future rouging. Products like Citrisurf 3050 are widely used due to their safety, environmental friendliness, and compliance with ASTM A967 standards.
Frequency of Maintenance: Monthly, Quarterly, or Per Cycle?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer to pipeline maintenance. Instead, facilities should determine schedules based on:
Frequency of product changeovers
Type of formulation
Operating temperature and steam usage
Regulatory audit history
Some plants integrate quarterly cleaning and passivation into their preventive maintenance schedules, while others prefer per-batch evaluation, especially when dealing with high-potency activities or sensitive biologics.
The Role of Inline Passivation Systems
Modern pharmaceutical facilities are adopting in-line passivation systems that clean, derouge, and passivate pipelines without dismantling. These systems:
Save labor costs
Minimize downtime
Improve consistency
Enable validation for every cleaning cycle
This is especially useful when using Citrisurf 3050 or other derouging chemicals that are NSF certified and compliant with pharmaceutical-grade surface treatment.
Conclusion: The Future of Stainless Steel Maintenance in Pharma
As pharmaceutical production becomes more advanced and regulated, ensuring the integrity of stainless steel piping systems is paramount. Preventing and addressing rouging isn’t merely a maintenance task—it’s a critical aspect of product safety, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Investing in proper cleaning, derouging and passivation, using advanced products like Citrisurf 3050, and adhering to industry standards like ASTM A380/A967 ensures a long lifecycle for your SS316L pipelines.
More importantly, it guarantees that your pharma products remain uncompromised, aligning with the ultimate goal of delivering safe and effective therapies to patients around the globe.

